- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Science & Programming
easy quicksort tutorial with Java/C/C++ examples
What's the Quicksort?
Quicksort is a fast and reliable method of sorting data, the quicksort (without any kind of refinaments) is very simple to write but it still is a very fast sorting algorithm compared to other algorithms such as the bubblesort.
In the video on the right you can watch some sorting algorithms and you will see the performance of the quicksort against the other algorithms, but quicksort has its own "flaws" which are referred below.
The quicksort was invented by Charles Antony Richard Hoare in 1960
Explaining the Quicksort
- PIVOT: The first thing that you have to do is selecting a pivot, a pivot is any number of the array that you want to sort, it can be the last, the first, the middle one, it has no criteria to be selected.
- PARTITION: This is for me the hardest part to explain and to understand, so i'll try to be clear enough. Think in a partition like an array, in this array you will start with a pointer at the beginning (the i), and with one pointer at the end (the j).
What you will do with the i is travel through the array forward until you find an element that is equal or greater than the pivot.
With the j you will travel through the array backward until you find an element that is equal or smaller than the pivot.
while (i <= j)
{
while (arr[i] < pivot)
i++;
while (arr[j] > pivot)
j--;
//continue...Then after you found both numbers, you will swap them only if this condition "i<=j" is true, which means that the two pointers haven't met or crossed each other yet, so there are some numbers left to analyze.
//...continuation
if (i <= j)
{
tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
i++;
j--;
}
};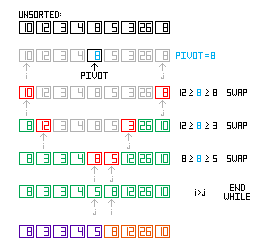
After you have done this, you will realize that you have your array divided in two non-equal parts, left with numbers equal or smaller than the pivot and on the right with numbers equal or greater than the pivot.
The picture on the left demonstrates what we have done so far with an example.
(click on it to get the full view)
- RECURSION: Then recursively sort the new partition of smaller elements, and then the partition of greater elements.
if (left < j) //left is the begin of the array quickSort(arr, left, j); if (i < right) //right is the end of the array quickSort(arr, i, right);
C/C++ Example
void quickSort(int arr[], int left, int right) {
int i = left, j = right;
int tmp;
int pivot = arr[(left + right) / 2];
/* partition */
while (i <= j) {
while (arr[i] < pivot)
i++;
while (arr[j] > pivot)
j--;
if (i <= j) {
tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
i++;
j--;
}
};
/* recursion */
if (left < j)
quickSort(arr, left, j);
if (i < right)
quickSort(arr, i, right);
}This example isn't mine but i have used it before and it works, the parameters of the method are the array, the start postion which is commonly 0, and the size of the array -1.
As far as i know you only have to take the "void" from the method and it will work for C.
(the link below will redirect you to the page where i get these code sample)
JAVA Example
static void quicksort(int array[], int begin, int end) {
int i = begin, j = end;
int pivot = array[end];
while (i <= j) {
while (array[i] < pivot)i++;
while (array[j] > pivot)j--;
if (i <= j) {
if (i != j) { //this is a swap of values
array[i] ^= array[j]; //without a use of an extra
array[j] ^= array[i]; //variable, it is a swap using
array[i] ^= array[j]; //the XOR operator, i used it
} //so you can learn it because i
i++; //think it is fun.
j--;
}
}
if (begin < j)
quicksort(array, begin, j);
if (i < end)
quicksort(array, i, end);
}This JAVA example i made it myself and i use the XOR operator to do the swap, when you use the swap with arrays you must verify if the to pointers i and j are not equal because it won't work if they are equal, to understand the XOR swap better open the link below.
Quicksort "flaws"
This presented quicksort isn't perfect actually it is the quicksort on is simplest form, because it has no kind of refinement it works as fast as a bubblesort in is worst case. An example will be an array with all of it's elements of the same value. If you give 1sec of thought about it you will see for every movement of i and j you will be realizing a swap.



